InViG 520K Dataset
We first sample and filter 21K images from OpemImages Dataset, based on which we recruit annotators to
label each image with one or more targets and human-to-human dialogues. With 21K labeled data, we further
develop an annotation system to automatically generate HRI data. We further generate 500K goal-oriented
disambiguation dialogues in extremely low costs. Therefore, in total, our InViG dataset contains more than
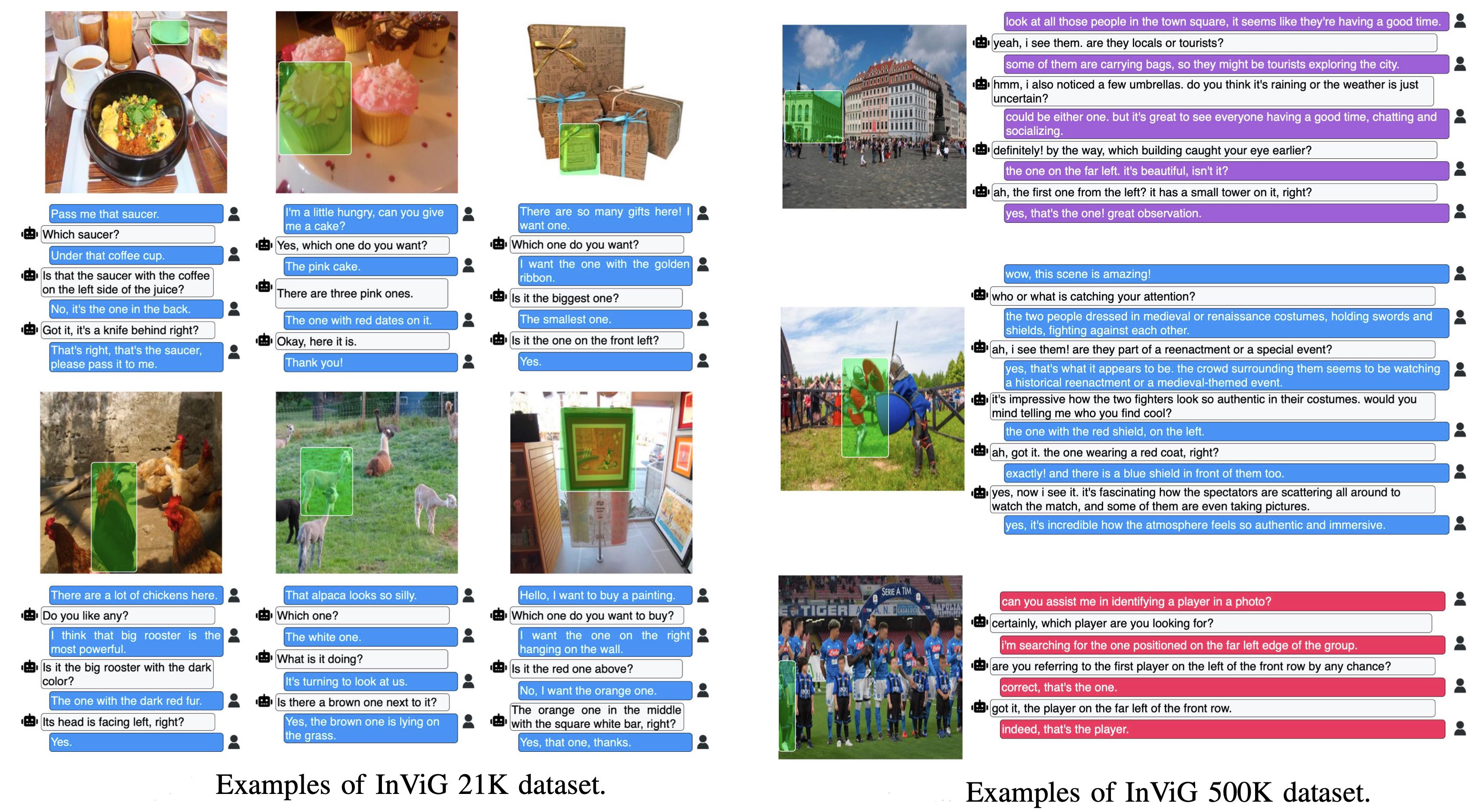
520K dialogues for interactive visual grounding. We demonstrate the comparison between InViG Dataset and
previous works in Table I. In summary, InViG dataset is proposed to solve the problem of object-oriented
open-ended interactive ambiguity in HRI, which widely appears in daily communications between humans.
Therefore, differentiated from all previous works, InViG dataset contains extensive interactive disambi
guation data to facilitate the development of HRI systems.
We first sample and filter 21K images from OpemImages Dataset, based on which we recruit annotators to label each image with one or more targets and human-to-human dialogues. With 21K labeled data, we further develop an annotation system to automatically generate HRI data. We further generate 500K goal-oriented disambiguation dialogues in extremely low costs. Therefore, in total, our InViG dataset contains more than 520K dialogues for interactive visual grounding. We demonstrate the comparison between InViG Dataset and previous works in Table I. In summary, InViG dataset is proposed to solve the problem of object-oriented open-ended interactive ambiguity in HRI, which widely appears in daily communications between humans. Therefore, differentiated from all previous works, InViG dataset contains extensive interactive disambi guation data to facilitate the development of HRI systems.
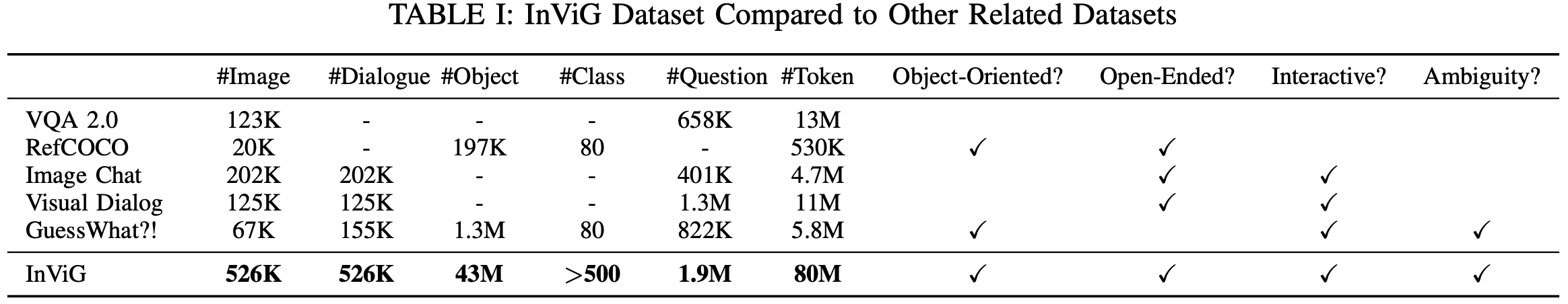
Some samples from InViG 21K and InViG 500K:
Some samples from InViG 21K and InViG 500K: